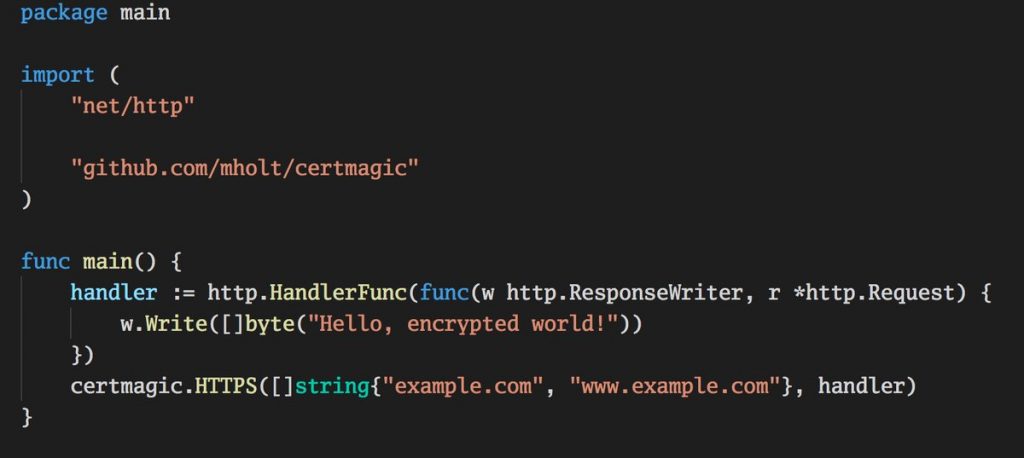
This is next level of dealing with certificates. Great job by Matt Hold and open source community on Certmagic module.
Read his twitter thread on the subject.

This is next level of dealing with certificates. Great job by Matt Hold and open source community on Certmagic module.
Read his twitter thread on the subject.
Hi all,
this is day 1 of 100 days I am coding one go program a day. Wish me good luck!
In this example I will show how to parse command line arguments with flag module and os.Args array.
Flag module is very powerful and can be as simple as this:
//...
import "flag"
//...
name := flag.String("user", "", "user name")
flag.Parse()
fmt.Printf("user name is %s\n", *name)
To have the “same” functionality with os.Args you have to do some work. In following example I added support for –user, -user and user=<value> arguments.
//...
import "os"
//...
var userArg string
for index, arg := range os.Args {
pattern := "-user="
x := strings.Index(arg, pattern)
if x > -1 {
userArg = arg[x+len(pattern):]
continue
}
if arg == "-user" || arg == "--user" {
userArg = os.Args[index+1]
continue
}
}
fmt.Printf("user name is %s", userArg)
Full code:
package main
import (
"flag"
"fmt"
"os"
"strings"
)
func main() {
name := flag.String("user", "", "user name")
flag.Parse()
fmt.Printf("user name is %s\n", *name)
var userArg string
for index, arg := range os.Args {
pattern := "-user="
x := strings.Index(arg, pattern)
if x > -1 {
userArg = arg[x+len(pattern):]
continue
}
if arg == "-user" || arg == "--user" {
userArg = os.Args[index+1]
continue
}
}
fmt.Printf("user name is %s", userArg)
}
Latest code examples see on GitHub